Post Modernism, a style of architecture beginning in 1965 with the publication of Robert Venturi’s Complexity and Contradiction in Architecture and extending to 1989, has always elicited great public debate on the architectural merits of its built works perhaps best exemplified in the controversy over one of the most iconic Post Modern buildings, Michael Graves’ Public Service Building (aka the Portland Building).
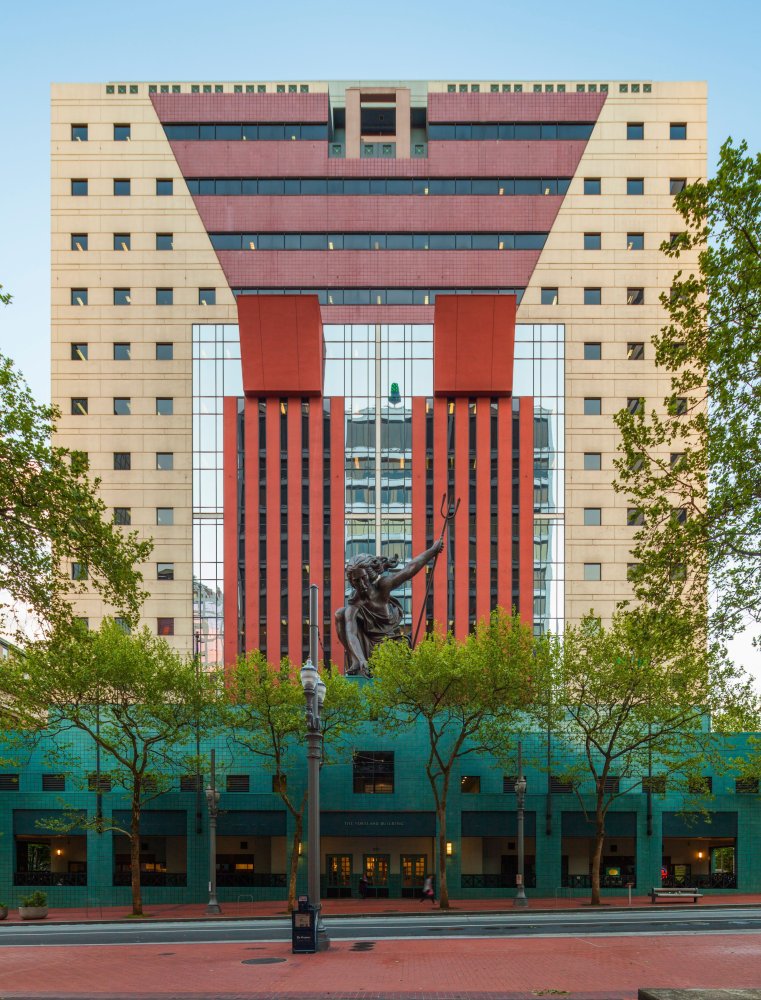

Whether or not Post Modern architecture is considered merely flamboyant superficial decoration or serious building design and genuine work is greatly debated. The debate, beginning a mere thirty years after the apex of the style, has arrived sooner than expected and focuses on the distinction between design and architecture. Whether or not the materials and assemblies used to construct the buildings are impermanent remain to be assessed, understood, and judged over a longer duration of time. Therefore, are material conservators and preservation technologists ready (and willing) to contribute a scientific approach and unbiased assessment to a controversial debate over a design style?
Post Modern design was broadly practiced in both the United States and internationally. Large and small firms were attracted to the stylistic incorporation of classical western design vocabulary in stark juxtaposition against the plain, unadorned, square box that many argued architecture had become. Design magazines published examples of Post Modern buildings ranging from the academic and scholar approach by architects like the Italian Aldo Rossi to the flamboyant American style creator Philip Johnson, as well as, buildings by architects only known on local and regional levels.

Architects, engineers, and material suppliers were pushing new materials and innovative construction technologies as a way to create Post Modern design elements. Continuous innovation in building skins reintroduced porcelain enamel panels, a product brought by Lustron to the building industry during the housing boom following World War II. New skins made from Glass Fibre Resin (GFR) capable of being molded in classical curves and ornamental shapes favored by Post Modern design were created. Innovations in brick technology including large scale brick panels made from a single wythe of masonry to panels whose outer face was only one half inch of masonry, or thin bricks. Improvements in resins created new wood or simulated wood products and adhesives for mounting faux finishes to structural systems. Perhaps one of the more ubiquitous new materials used in the creation of Post Modern architecture was the faux stucco product Dryvit, and Exterior Finish Insulation System (EIFS). Like porcelain enamel panels, EIFS were introduced as insulated wall assemblies as a means to improve energy performance during the world’s energy crisis of the 1970s.
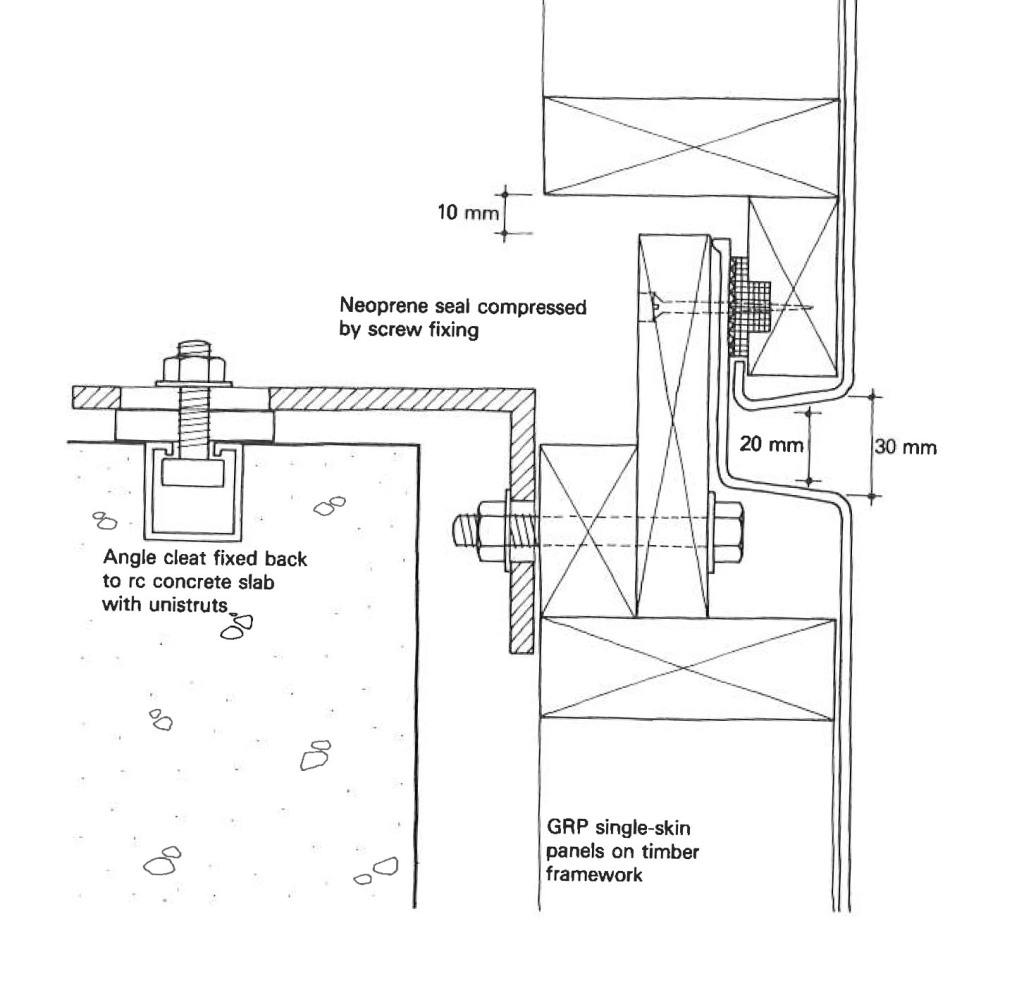
As Post Modern buildings reach thirty and fifty years, systems and products are aging and, like all older buildings, significant investments or improvements to infrastructure systems are often needed. Compared to more recent material innovations, Post Modern building performance levels are low and some of the innovative materials resulted in long-term material failures. As it is with any building skin, often the deficiencies of one material are in combination with more robust materials or the failing components are critical to the character defining features of the Post Modern design. And when material failure is coupled to design aesthetics and those aesthetics do not offer universal appeal, questions arise as to the merits of retaining the component. But should subjective opinions about design, a very personal matter compared to one’s appreciation of art, drive decisions to preserve or demolish a building? And when the building carries international recognition as a work of architecture, or as a work that defines the Post Modernism, should more resources be given to its preservation? Does the inherent impermanence of the original materials justify an approach of non-preservation as preservation? Many Post Modern buildings incorporate systems or components that are neither produced nor currently assembled in similar manners due to improvements in technology and building envelope science. Therefore, the process and method of building envelope repair could dramatically impact the exterior character of Post Modern structures.

Is the proper approach to retain the essence of criticism towards Post Modernism by preserving the appearance of insubstantial material installed incorrectly? Proposals to improve envelope performance of both the individual components and building systems are challenged in finding products that will both improve performance and retain the aesthetics of a Post Modern building. Like previous building styles and periods, the preservation of character defining elements that were originally inadequately or incorrectly produced or assembled has always been a source of preservation controversy. In preservation and the undersized windows of the Portland Building are defining elements of the Post Modern design. The preservation community should be prepared to participate in discussing the merits of Post Modernism. The conversation has begun.
Written by Peter Meijer AIA, NCARB, Principal.