In March 2015, we wrote about PDX Post Modern and Mid-Century Modern architecture, which to our eyes was being referenced by local architectural firms for their new designs located at the Burnside Bridgehead and elsewhere. A year later and the City of Portland is continuing to build, build, build especially around the Burnside Bridgehead. In addition, cries for the demolition of a Post Modern icon of architecture: Michael Grave’s designed, Portland Public Service Building, have turned into a proposed $200 million design-build project. Has Portland come to appreciate its architectural heritage from the recent past?

Portland Building, PacWest Center, Koin Tower
DoCoMoMo_Oregon, a local chapter of DoCoMoMo_US, is a non-profit organization dedicated to promoting the interest, education, and advocacy of the architecture, art, landscape, and urban design of the Modern Movement. Recently the Board voiced concerns for the type of alterations proposed for the late modern (post modern!) PacWest Center designed by Hugh Stubbins & Associates / Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, which underwent a Design Advice. John Russell, the original developer of the project who chose Hugh Stubbins as the architect, from a shortlist that included Philip Johnson and Minoru Yamasaki, provided testimony that agreed with the design team that the retail in the building isn’t currently working, but that the building’s design isn’t the major contributor. Overall, the Design Commission encouraged the design team to treat the PacWest Center like a historic building, and use the Secretary of the Interior’s Standards as an approach for the renovation.
The Koin Tower, designed by ZGF Partnership in 1984, is one of the most prominent buildings in Portland’s downtown rising sky-line, and an example of Post Modern architecture. It is Post Modern with whimsical lines and historical references to Gothic, Spanish, and Deco architectural characteristics. (King, 106) However, unlike the Post Modern Portland Building (interiors designed by ZGF), the Koin Tower has been accepted for its architectural whimsy in a place with a known tag line, “Keep Portland Weird.”
And on a smaller scale that truly connects to placemaking, the Lovejoy Fountain Pavilion designed by Charles Moore in 1962 as part of Lawrence Halprin’s fountain sequence was thoughtfully restored in 2012.
Appreciating the Recent Past
So, has Portland come to appreciate its architectural heritage from the recent past? While these four examples offer a glimpse of optimism towards the maintenance and rehabilitation of architecture from the recent past, there is still an uphill battle towards the preservation and rehabilitation of Post Modern, Modern, and historic architectural resources. This is not an argument to save every resource, but it’s our responsibility to our present and future communities to have places rich in architectural resources from different movements of history- architecture rich in diversity. For architectural diversity contributes to our place making, culture, and identity. Let’s Keep Portland Architecture Weird by both adding to and maintaining and rehabilitating.
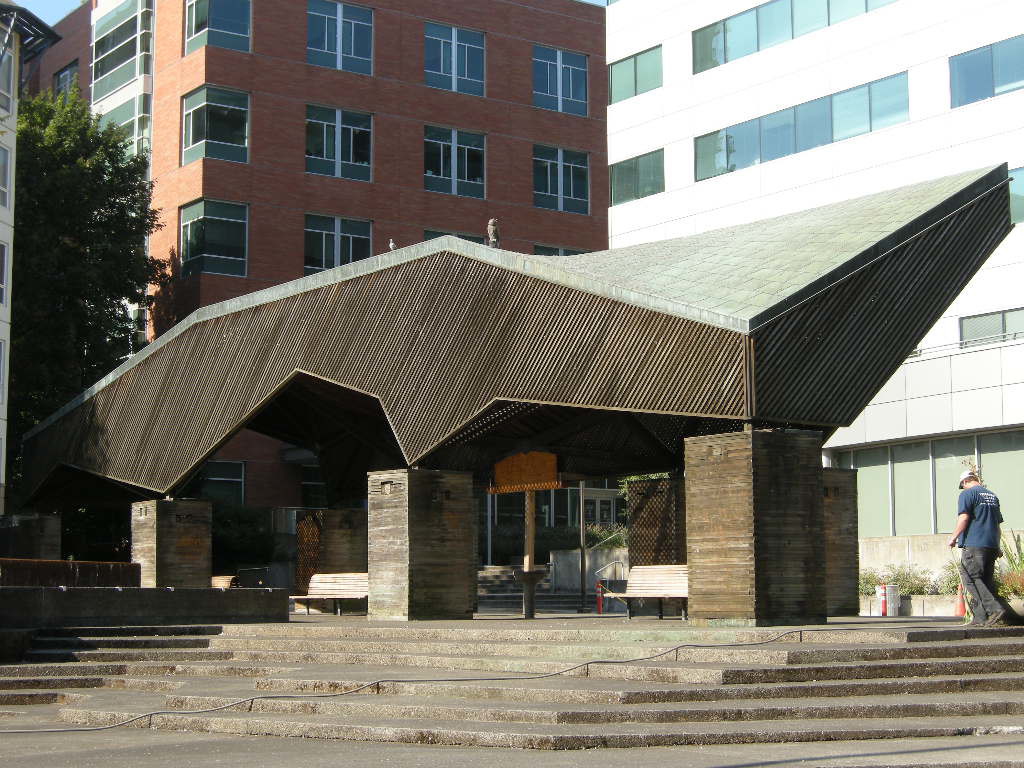

Lovejoy Pavilion
Written by Kate Kearney, Marketing Coordinator
———————————————————-
King, Bart. An Architectural Guidebook to Portland. 2nd ed. Corvallis: Oregon State University Press, 2007. Print.
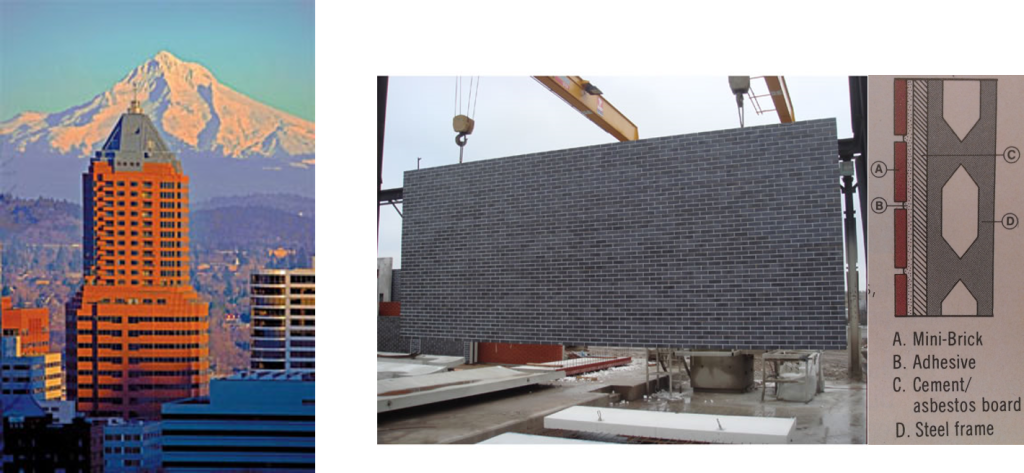
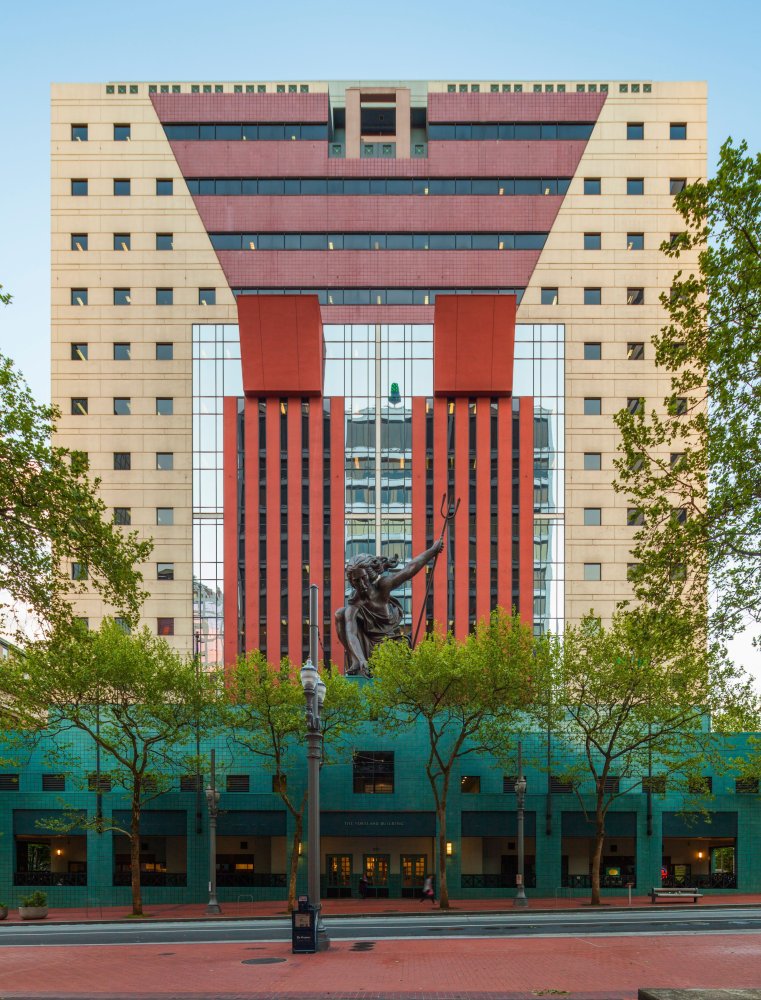
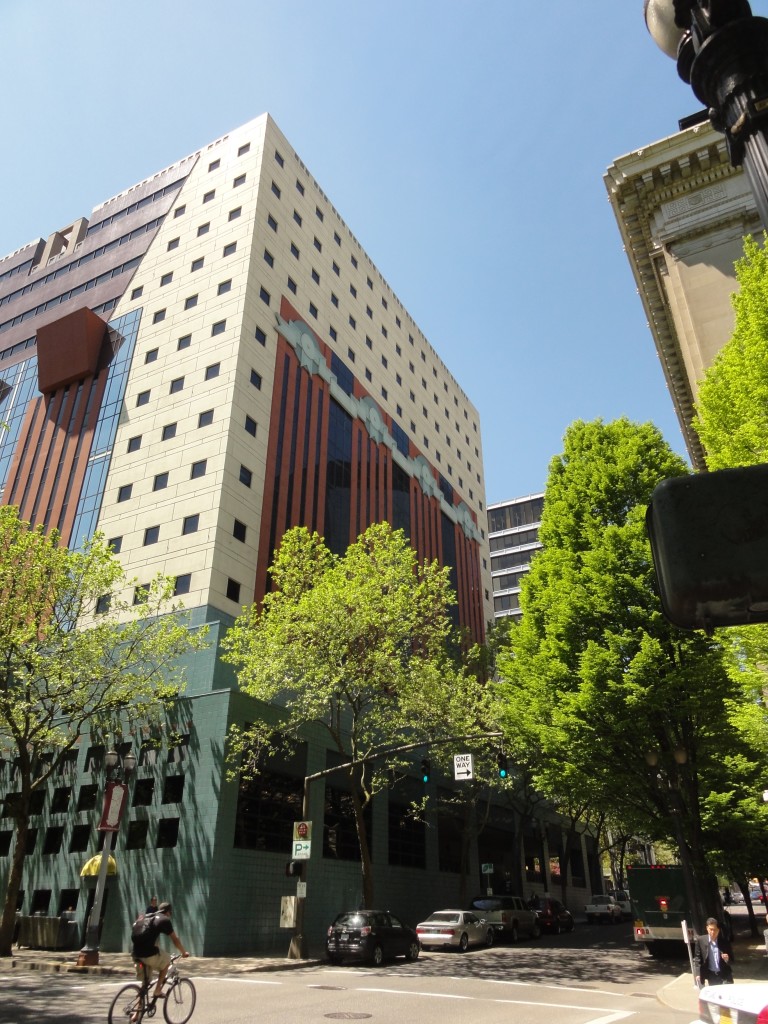



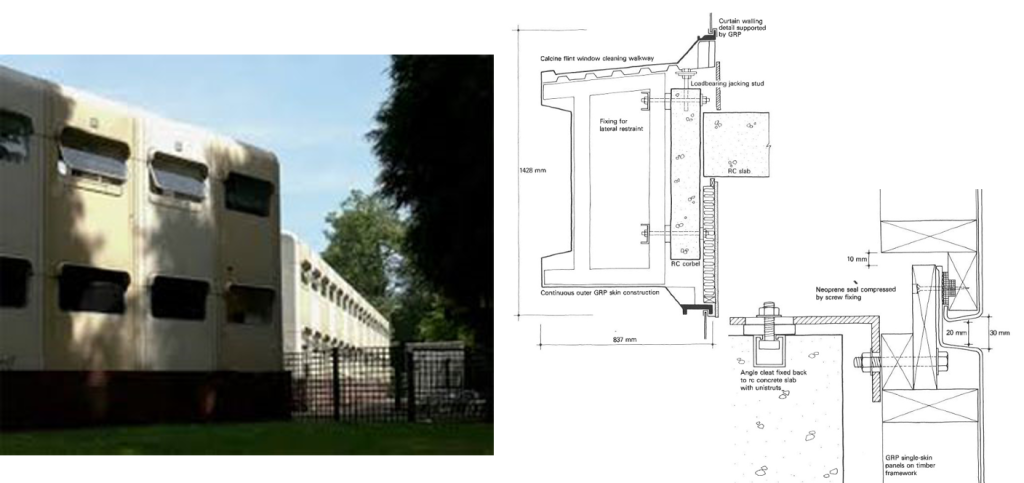



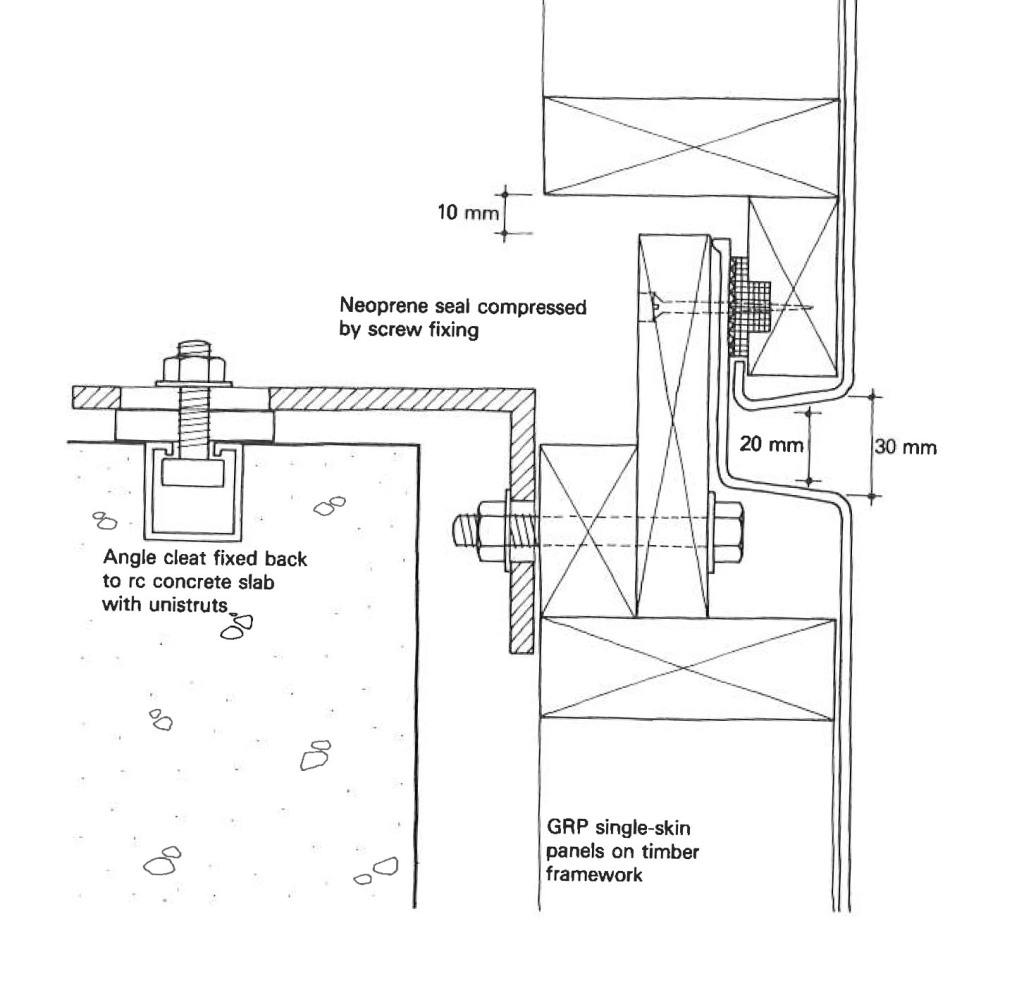

 The Portland Building itself is significant as one of a handful of high-profile building designs that defined the aesthetic of Post Modern Classicism in the United States between the mid-1960s and the 1980s. Constructed in 1982, the Portland Public Service Building is nationally significant as the notable work that crystallized Michael Graves’s reputation as a master architect and as an early and seminal work of Post-Modern Classicism, an American style that Graves himself defined through his work. The structure is ground-breaking for its rejection of “universal” Modernist principles in favor of bold and symbolic color, well-defined volumes, and stylized- and reinterpreted-classical elements such as pilasters, garlands, and keystones.
The Portland Building itself is significant as one of a handful of high-profile building designs that defined the aesthetic of Post Modern Classicism in the United States between the mid-1960s and the 1980s. Constructed in 1982, the Portland Public Service Building is nationally significant as the notable work that crystallized Michael Graves’s reputation as a master architect and as an early and seminal work of Post-Modern Classicism, an American style that Graves himself defined through his work. The structure is ground-breaking for its rejection of “universal” Modernist principles in favor of bold and symbolic color, well-defined volumes, and stylized- and reinterpreted-classical elements such as pilasters, garlands, and keystones.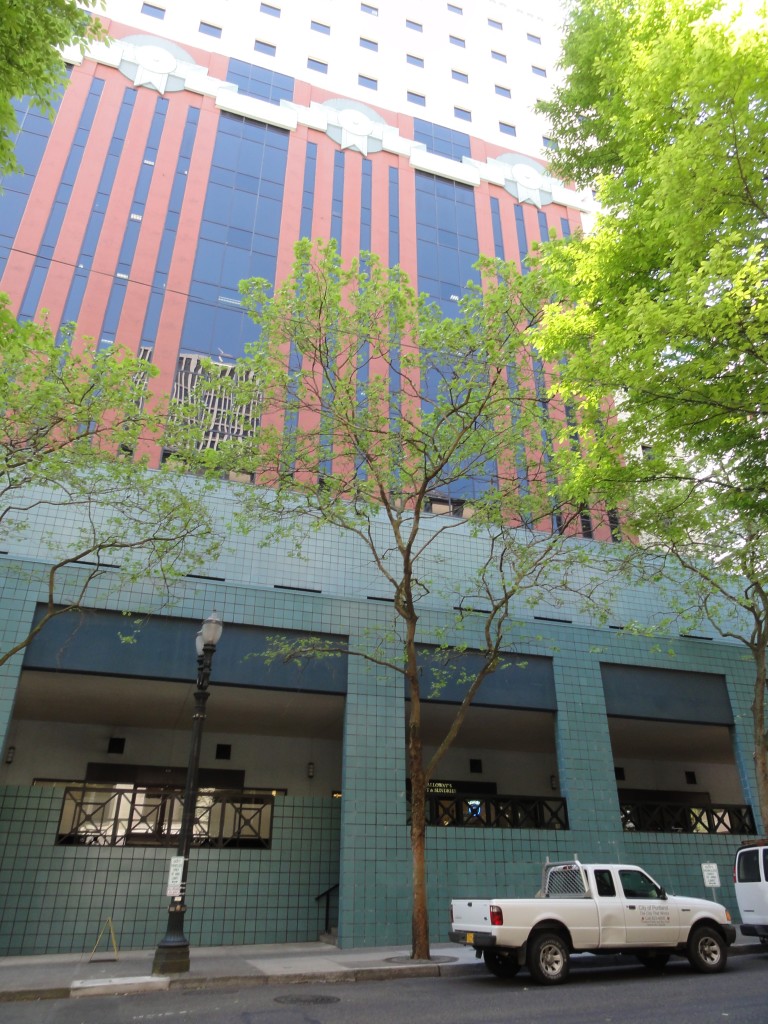  As one of the earliest large-scale Post-Modern buildings constructed, Graves’s design for the Portland Building was daring; almost shocking, in its vision for the future, and for its proposition as to what “after Modernism” could mean for architecture. The building itself is a fifteen-story regularly-fenestrated symmetrical monumental block clad in scored off-white colored stucco and set on a stepped two-story pedestal of blue-green tile. The building’s style is expressed through paint and applied ornament that implies classical architectural details, including terracotta tile pilasters and keystone, mirrored glass, and flattened and stylized garlands, among other elements that are intended to convey multiple meanings. For instance, the building is organized in a classical three-part division, bottom, middle, and top in reference to the human body, foot, middle, and head. At the same time, the building’s colors represent parts of the environment, with blue-green tile at the base symbolizing the earth and the light blue at the upper-most story representing the sky. The building uses layers of references to physically and symbolically tie it to place, its use, and the Western architectural tradition.
As one of the earliest large-scale Post-Modern buildings constructed, Graves’s design for the Portland Building was daring; almost shocking, in its vision for the future, and for its proposition as to what “after Modernism” could mean for architecture. The building itself is a fifteen-story regularly-fenestrated symmetrical monumental block clad in scored off-white colored stucco and set on a stepped two-story pedestal of blue-green tile. The building’s style is expressed through paint and applied ornament that implies classical architectural details, including terracotta tile pilasters and keystone, mirrored glass, and flattened and stylized garlands, among other elements that are intended to convey multiple meanings. For instance, the building is organized in a classical three-part division, bottom, middle, and top in reference to the human body, foot, middle, and head. At the same time, the building’s colors represent parts of the environment, with blue-green tile at the base symbolizing the earth and the light blue at the upper-most story representing the sky. The building uses layers of references to physically and symbolically tie it to place, its use, and the Western architectural tradition.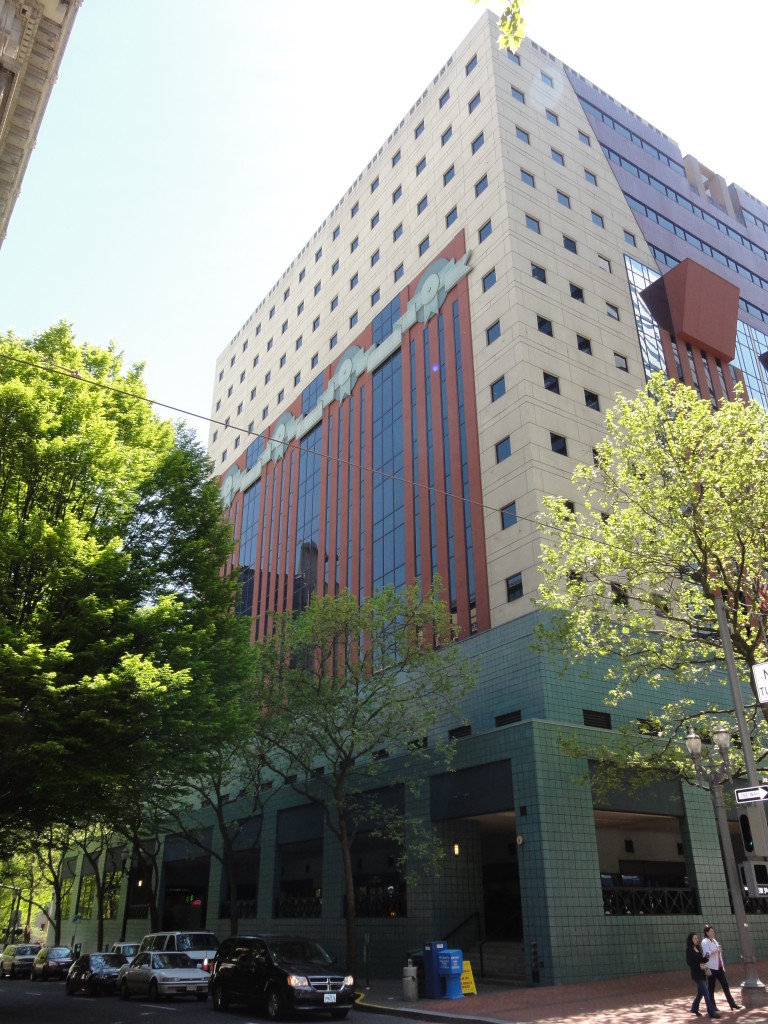 The boxy, fifteen-story building is located in the center of downtown Portland, Oregon, occupying a full 200 by 200-foot city block right next to City Hall. The Portland Building is a surprising jolt of color within the more restrained environment and designs of nearby buildings, with its blue tile base and off-white stucco exterior accented with mirrored glass, earth-toned terracotta tile, and sky-blue penthouse. The figure of Lady Commerce from the city seal, reinterpreted by sculptor Ray Kaskey to represent a broader cultural tradition and renamed ‘Portlandia,’ is placed in front of one of the large windows as a further reference to the city. The building is notable for its regular geometry and fenestration as well as the architect’s use of over-scaled and highly-stylized classical decorative features on the building’s facades, including a copper statue mounted above the entry, garlands on the north and south facades, and the giant pilasters and keystone elements on the east and west facades. Whether or not one judges the building to be beautiful or even to have fulfilled Graves’s ideas about being humanist in nature, it is undeniably important in the history of American architecture. The building has been dispassionately evaluated in various scholarly works about the history of architecture and is inextricably linked to the rise of the Post-Modern movement.
The boxy, fifteen-story building is located in the center of downtown Portland, Oregon, occupying a full 200 by 200-foot city block right next to City Hall. The Portland Building is a surprising jolt of color within the more restrained environment and designs of nearby buildings, with its blue tile base and off-white stucco exterior accented with mirrored glass, earth-toned terracotta tile, and sky-blue penthouse. The figure of Lady Commerce from the city seal, reinterpreted by sculptor Ray Kaskey to represent a broader cultural tradition and renamed ‘Portlandia,’ is placed in front of one of the large windows as a further reference to the city. The building is notable for its regular geometry and fenestration as well as the architect’s use of over-scaled and highly-stylized classical decorative features on the building’s facades, including a copper statue mounted above the entry, garlands on the north and south facades, and the giant pilasters and keystone elements on the east and west facades. Whether or not one judges the building to be beautiful or even to have fulfilled Graves’s ideas about being humanist in nature, it is undeniably important in the history of American architecture. The building has been dispassionately evaluated in various scholarly works about the history of architecture and is inextricably linked to the rise of the Post-Modern movement.