PMA is surveying and documenting the Laurelhurst neighborhood for a current project. Below is an overview of the typical residential architectural styles found throughout the neighborhood, with a brief introduction on its development.
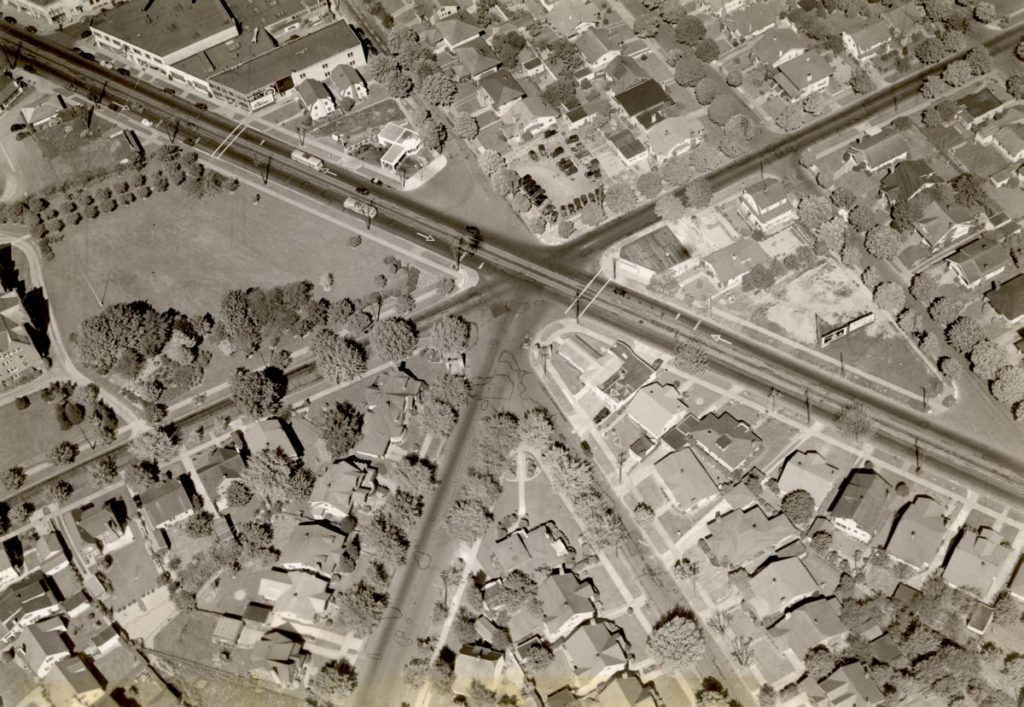
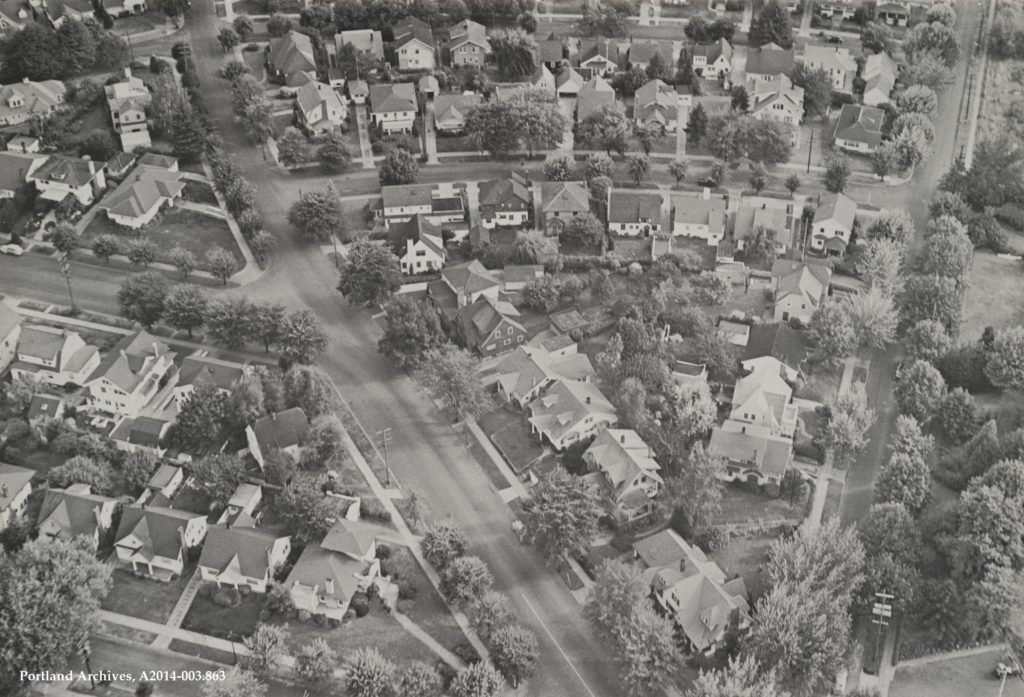
Laurelhurst is a 442-acre residential neighborhood in Portland, Oregon, located thirty-two city blocks east of the Willamette River. Most of the neighborhood is in northeast Portland, with only the southernmost quarter, below E Burnside Street, in southeast Portland. César E Chávez Boulevard, originally called NE 39th Street, runs north to south, dividing the neighborhood into two halves. The original 1909/10 plat boundaries of the Laurelhurst neighborhood were generally bounded by NE 32nd and 44th Avenues, and NE Halsey and SE Stark Streets. Construction of the Banfield Freeway (I-84) has had a major impact on the northern portion of the neighborhood, separating the northeastern corner of the original plat from the rest of Laurelhurst.

DEVELOPMENT
The development of the neighborhood was a result of the extension of city streetcar lines to the east side of the river, enabling a tremendous population increase in this area right before 1909. The layout and development of the Laurelhurst neighborhood was strongly influenced by the national City Beautiful movement. This social movement was initially a crusade for reforms in many facets of public and private life, pushing for food and water systems, schools, and cities to be more healthful and science-based in the period after the Industrial Revolution.
The neighborhood demonstrates the results of Portland’s early transit system that triggered the city’s expansion and enabled family life to be removed from the center of the city yet efficiently connected to the downtown hub of business and commerce. In this sense it was a true suburb, representing an idealized plan for residential living. The curvilinear streets were laid out with an eye for beauty as well as harmony between the structures and the environment. Laurelhurst remains one of Portland’s oldest intact East Side neighborhoods, and illustrates an era of tremendous suburban growth in Portland’s history, made possible by streetcar networks.
Economic Trends 1900 – 1970
The Lewis & Clark Exposition, in 1905, marked the beginning of a period of prosperity and growth for Portland. Portland’s population almost doubled in the single five-year period from 1905-1910, from 110,929 to 207,214 residents.[1] Laurelhurst’s population continued to increase until the onset of the Great Depression in 1929, when homebuying and development reached a low once again until just after 1940. This mirrored the trend across the United States during the Depression years, with a 95% drop in new home construction from 1925 to 1933. The 1940’s marked a period of major economic development, mainly due to advancements in the automobile industry. As a result of the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1921, the rising popularity of cars in the 1930’s, and the post-WWII recovery from the Great Depression, residents of Portland could live much further away from their jobs than they could even with the development of streetcars only thirty years prior. Suburban development and lifestyles became even more appealing. Portland experienced another period of economic decline during the Vietnam War from 1955 to 1975. In particular, property values in Laurelhurst plummeted in the 1970’s, to below average at best, and often below the cost of affordable low-income housing in the city.

ARCHITECTURE
Building restrictions maintained Laurelhurst’s reputation as a desirable neighborhood. The homes encompassed a controlled variety of architectural styles, so much so that a brochure was given to families upon purchasing a lot for the types of styles that were recommended for development. Recommended styles in Murphy’s promotional materials of the time included “Pure Italian, Japanese, Old English, Swiss Chalet, Colonial, New England, or Spanish Mission.”[2] This variety of architectural styles contributed to Laurelhurst’s reputation as a “neighborhood of character”; this aesthetic holds true as the majority of styles and examples in Laurelhurst retain their material and stylistic integrity.
A single block, located in the southeastern quadrant of the neighborhood between SE Ash and E Burnside, was developed by the Laurelhurst Company as a showcase for bungalows.[3] This block was named Fernhaven Court, called “bungalow fairyland,” and still has many of its original features today. Some of these 1915-1925 Fernhaven Court bungalows have a noticeable Japanese design influence. The block also has a twenty-foot alleyway through the middle, one of only two alleys in Laurelhurst.
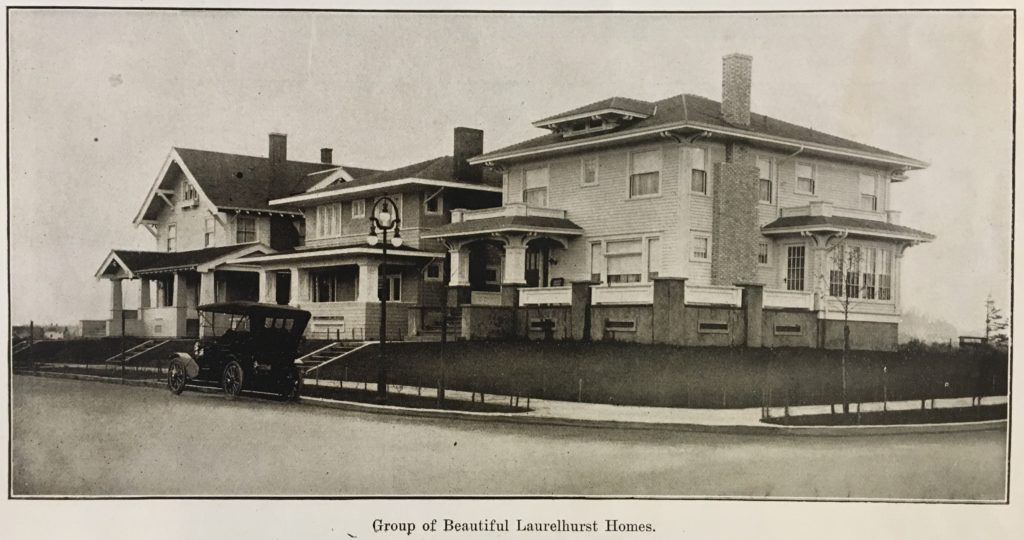
In the southwestern quadrant, the west end of the block bounded by NE Couch, NE Davis, NE Laurelhurst Place, and NE Cesar E. Chavez Blvd was designed as “The Laurelhurst Group of Cottages,” nine homes laid out and designed by architects Ellis Lawrence and W.M. Holford with George Otten, landscape designer. Five of these were built by 1919, with a “central garden” divided by shrubs and specifying “service uses” screened by lattice. The homes, constructed by the Laurelhurst Company, are in English Cottage style.
Paul Murphy’s own house at 3574 E. Burnside, also designed by Lawrence & Holford, received accolades for its “picturesque” design in the July 1919 issue of “The House Beautiful.” By November of that year the house was named one of the ten best examples of architecture in Portland by that same publication.[4]

Typical Neighborhood Architectural Styles
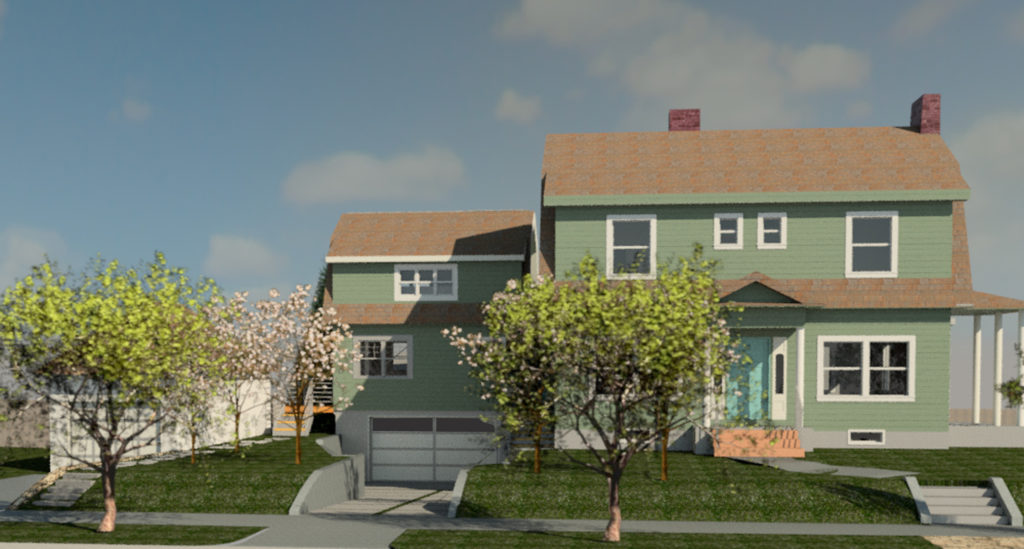
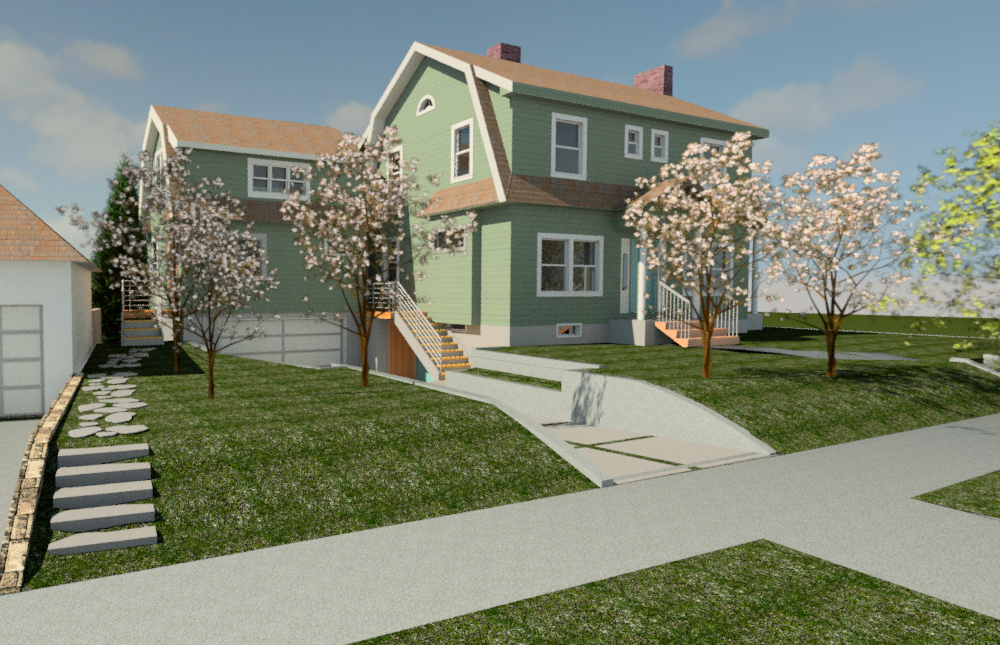
A majority (88%) of resources in Laurelhurst date between 1910 and 1932, and the architectural styles of the neighborhood reflect that majority; the first property owners of Laurelhurst were restricted in their choices for designs, which aimed to create a cohesive and more desirable neighborhood appearance. The most prevalent architectural styles identified in Laurelhurst are Craftsman (42%), Colonial Revival (36%), and English Cottage (19%). Some houses do have a combination of styles so percentages will add up to more than 100% of resources. Other identified styles from that era include Prairie School, Tudor Revival, Mediterranean Revival, Neo-Classical; later architectural styles observed within Laurelhurst include Minimal Traditional, World War II-Era Cottage, and Ranch.

Prevalent Building Use and Typology
Across the United States from the 1890s into the 1920s as the ideal suburban home was being refined and developed, houses were becoming more technologically innovative and less formal in layout. Two principal house typologies emerged during this period, the bungalow and the American Foursquare. Both of these were often mass-produced and offered for sale by catalog. Bungalows offered an affordable house type for a family without servants. The typical bungalow is one or one-and-a-half stories, with a broad, shallowly-pitched roof and a wide open front porch across the full front or most of the front of the house. While bungalows can be in English Cottage or Mission Revival styles, they are most often associated with the Craftsman style and the California Arts and Crafts movement. A typical Foursquare is boxy and more vertical in form, usually two to two-and-a-half stories in height. A single-height porch runs across most or all of the front of the house, and the layout is generally four major rooms on each level. Like bungalows, Foursquare houses can appear in a variety of styles.[5] The Colonial Revival style predominates in some areas, but in the Pacific Northwest the Craftsman Foursquare is by far the most prevalent style.
After WWI, the trend for single-family homes across the U. S. was generally smaller. A variety of period revival styles appeared in the 1920s as bungalows or period cottages. Most common were the English Cottage or English Tudor as well as Colonial revival styles ranging from Dutch, English, French, and Spanish. A period cottage is generally no more than one-and-a-half story, and has a small street–fronting façade but may extend back on its lot to create a long, narrow footprint.
Written by Kristen Minor / Associate, Preservation Planner with Marion Rosas / Designer
Download Laurelhurst Architectural Styles.
Footnotes
1. K. Zisman et al, Portland Oregon’s Eastside Historic and Architectural Resources, 1850-1938 (United States Department of the Interior, 1988, as amended 2012, edited by Timothy Askin and Ernestina Fuenmayor), E:10.
2. “Laurelhurst and its Park,” 22.
3. A bungalow can be described as a small house, low and broad in form, with a wide front porch and spreading eaves. They are most often Craftsman in style.
4. Rene Marshall, “In Portland, Oregon,” The House Beautiful vol 46, July 1919, 30-31 and Helen Eastham, “Best Examples of Architecture in Portland, Oregon,” The House Beautiful vol. 46, Nov 1919, 308-310, 336.
5. McClelland et al, 56.
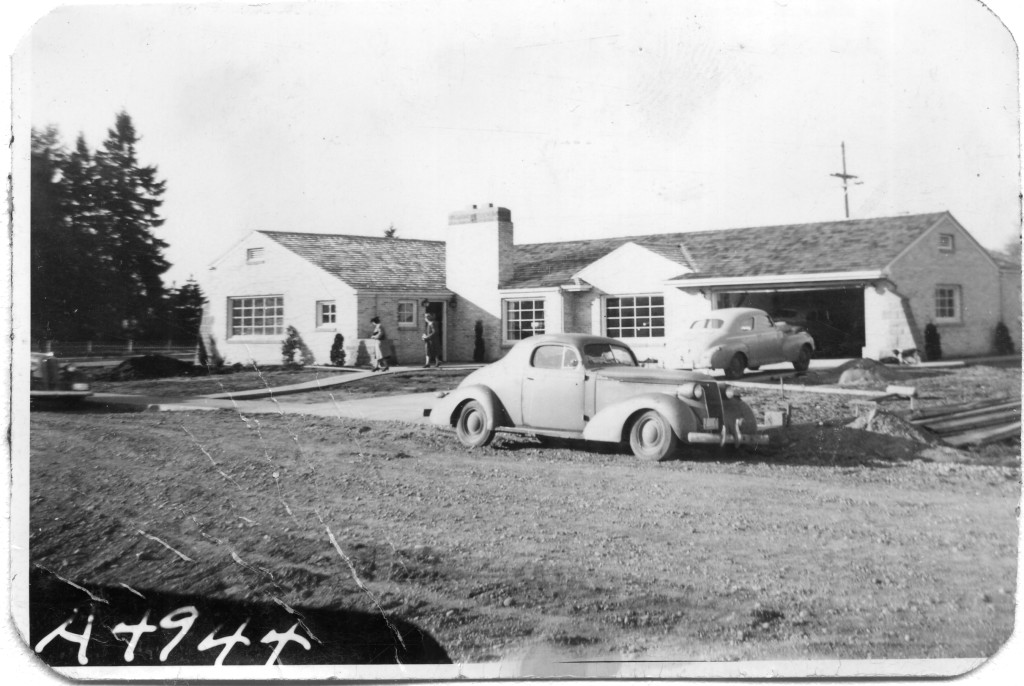









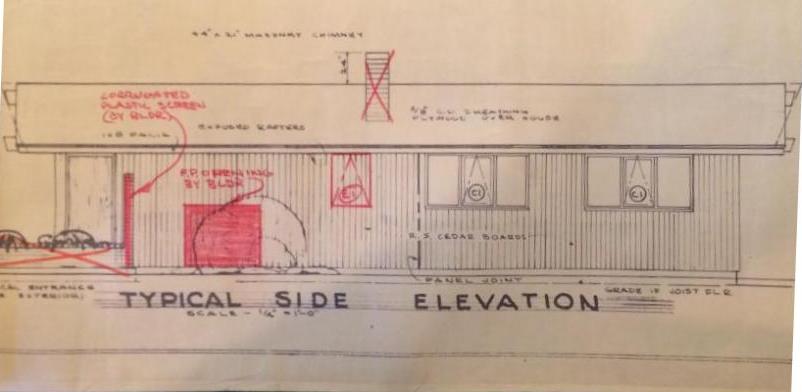
 Buildings constructed before 1965 have reached the age of eligibility for being considered historic by the standards of the National Register. That means that much of Modern Architecture, the general period ranging from 1950 through 1970, is historic, or soon will be considered historic as the 50-year mark is crossed. As historians assess and study Modern Architecture, we provide ever more precise descriptions and terms to describe the sub-styles and variations within the large umbrella term, “Modern.” As in taxonomy, which classifies and categorizes living organisms, we can recognize and assign groups of similar resources together for study.
Buildings constructed before 1965 have reached the age of eligibility for being considered historic by the standards of the National Register. That means that much of Modern Architecture, the general period ranging from 1950 through 1970, is historic, or soon will be considered historic as the 50-year mark is crossed. As historians assess and study Modern Architecture, we provide ever more precise descriptions and terms to describe the sub-styles and variations within the large umbrella term, “Modern.” As in taxonomy, which classifies and categorizes living organisms, we can recognize and assign groups of similar resources together for study.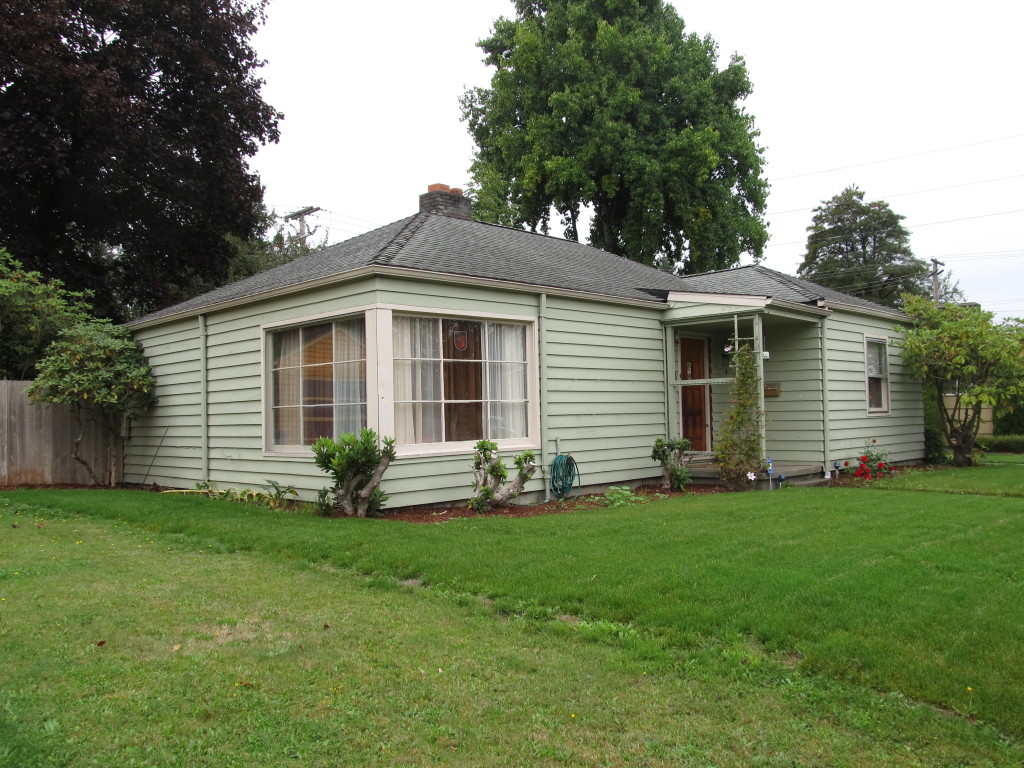 
 The Olympia survey classified the first grouping of styles as those that are transitional. Transitional Modern styles have some elements of Modern and some elements of more traditional architecture. Windows might be vertically-oriented, double-hung wood windows (traditional) rather than having horizontal proportions (Modern). A roof might be a moderate pitch, with minimal overhangs (traditional), rather than a shallow pitch with outwardly-extending gables (Modern). In Olympia, 37% of the houses surveyed were Modern Minimal Traditional, by far the most prevalent Transitional Modern style.
The Olympia survey classified the first grouping of styles as those that are transitional. Transitional Modern styles have some elements of Modern and some elements of more traditional architecture. Windows might be vertically-oriented, double-hung wood windows (traditional) rather than having horizontal proportions (Modern). A roof might be a moderate pitch, with minimal overhangs (traditional), rather than a shallow pitch with outwardly-extending gables (Modern). In Olympia, 37% of the houses surveyed were Modern Minimal Traditional, by far the most prevalent Transitional Modern style.  Ranch style architecture is the style that architecture critics have generally spurned, since houses were often constructed by contractors without architect’s involvement. Ranch buildings are broad, one-story, and horizontal in overall proportion. They have an attached garage which faces the street and is part of the overall form of the house, and almost always a large picture window facing the street as well. Cladding is used to accentuate the horizontal lines of the house, so there is often a change in material at the lower part of the front façade- brick veneer was a popular choice. Many of the sub-styles of Ranch architecture are “styled” Ranch houses, meaning that elements from another style of architecture were placed on a Ranch form building. One example is Storybook Ranch, which uses “gingerbread” trim, dormers or a cross-gable, and sometimes diamond-pane windows. Are these decorated sub-styles still part of the canon of Modern Architecture? In many ways, they are more Post-Modern than Modern, but that distinction is worthy of an involved discussion of its own.
Ranch style architecture is the style that architecture critics have generally spurned, since houses were often constructed by contractors without architect’s involvement. Ranch buildings are broad, one-story, and horizontal in overall proportion. They have an attached garage which faces the street and is part of the overall form of the house, and almost always a large picture window facing the street as well. Cladding is used to accentuate the horizontal lines of the house, so there is often a change in material at the lower part of the front façade- brick veneer was a popular choice. Many of the sub-styles of Ranch architecture are “styled” Ranch houses, meaning that elements from another style of architecture were placed on a Ranch form building. One example is Storybook Ranch, which uses “gingerbread” trim, dormers or a cross-gable, and sometimes diamond-pane windows. Are these decorated sub-styles still part of the canon of Modern Architecture? In many ways, they are more Post-Modern than Modern, but that distinction is worthy of an involved discussion of its own.  The Olympia Mid-Century Residential survey found over half the resources surveyed to be Ranch or variants of Ranch style. 31% of the surveyed homes were identified as simply Ranch, with another 11% Early Ranch, 9% Contemporary Ranch, 4% Split-Level or Split-Entry, and 4% one of the “Styled” Ranch variations. Sheer numbers alone remind us that the Ranch is deserving of study and shows us how the majority of middle-class Americans lived. As Alan Hess writes in his book Ranch House,
The Olympia Mid-Century Residential survey found over half the resources surveyed to be Ranch or variants of Ranch style. 31% of the surveyed homes were identified as simply Ranch, with another 11% Early Ranch, 9% Contemporary Ranch, 4% Split-Level or Split-Entry, and 4% one of the “Styled” Ranch variations. Sheer numbers alone remind us that the Ranch is deserving of study and shows us how the majority of middle-class Americans lived. As Alan Hess writes in his book Ranch House,